Bradshaw, C.J.A., & Brook, B.W. (2009). The Cronus Hypothesis – extinction as a necessary and dynamic balance to evolutionary diversification Journal of Cosmology, 2, 201-209 (free online access)
Bradshaw, C.J.A., & Brook, B.W. (2009). The Cronus Hypothesis – extinction as a necessary and dynamic balance to evolutionary diversification Journal of Cosmology, 2, 201-209 (free online access)
——————————————————
As described on ConservationBytes, we (Corey Bradshaw and Barry Brook), and I recently published a paper in the very new and perhaps controversial online journal , the Journal of Cosmology. Cosmology? According the journal, ‘cosmology’ is:
“the study and understanding of existence in its totality, encompassing the infinite and eternal, and the origins and evolution of the cosmos, galaxies, stars, planets, earth, life, woman and man”.
The journal publishes papers dealing with ‘cosmology’ and is a vehicle for those who wish to publish on subjects devoted to the study of existence in its totality.
Ok. Quite an aim.
Our paper is part of the November (second ever) issue of the journal entitled Asteroids, Meteors, Comets, Climate and Mass Extinctions, and because we were the first to submit, we managed to secure the first paper in the issue.
Our paper, entitled The Cronus hypothesis – extinction as a necessary and dynamic balance to evolutionary diversification, introduces a new idea in the quest to find that perfect analogy for understanding the mechanisms dictating how life on our planet has waxed and waned over the billions of years since it first appeared.
 In the 1960s, James Lovelock conceived the novel idea of Gaia – that the Earth functions like a single, self-regulating organism where life itself interacts with the physical environment to maintain conditions favourable for life (Gaia was the ancient Greeks’ Earth mother goddess). (see here for a book review on BNC of Lovelock’s latest, “The Vanishing Face of Gaia“) Embraced, contested, denounced and recently re-invigorated, the idea has evolved substantially since it first appeared. More recently (this year, in fact), Peter Ward countered the Gaia hypothesis with his own Greek metaphor – the Medea hypothesis. Essentially this view holds that life instead ‘seeks’ to destroy itself in an anti-Gaia manner (Medea was the siblicidal wife of Jason of the Argonauts). Ward described his Medea hypothesis as “Gaia’s evil twin”.
In the 1960s, James Lovelock conceived the novel idea of Gaia – that the Earth functions like a single, self-regulating organism where life itself interacts with the physical environment to maintain conditions favourable for life (Gaia was the ancient Greeks’ Earth mother goddess). (see here for a book review on BNC of Lovelock’s latest, “The Vanishing Face of Gaia“) Embraced, contested, denounced and recently re-invigorated, the idea has evolved substantially since it first appeared. More recently (this year, in fact), Peter Ward countered the Gaia hypothesis with his own Greek metaphor – the Medea hypothesis. Essentially this view holds that life instead ‘seeks’ to destroy itself in an anti-Gaia manner (Medea was the siblicidal wife of Jason of the Argonauts). Ward described his Medea hypothesis as “Gaia’s evil twin”.
One can marvel at the incredible diversity of life on Earth (e.g., conservatively, > 4 million protists, 16600 protozoa, 75000-300000 helminth parasites, 1.5 million fungi, 320000 plants, 4-6 million arthropods, > 6500 amphibians, 10000 birds and > 5000 mammals) and wonder if there might be something in the ‘life makes it easier for life’ idea underlying Gaia. However, when one considers that over 99 % of all species that have ever existed are today extinct, then a Medea perspective might dominate.
Enter Cronus. Here we posit a new way of looking at the tumultuous history of life and death on Earth that effectively relegates Gaia and Medea to opposite ends of a spectrum. Cronus (patricidal son of Gaia overthrown by his own son, Zeus, and banished to Hades) treats speciation and extinction as birth and death in a ‘metapopulation’ of species assemblages split into biogeographic realms. Catastrophic extinction events can be brought about via species engineering their surroundings by passively modifying the delicate balance of oxygen, carbon dioxide and methane – indeed, humans might be the next species to fall victim to our own Medean tendencies. But extinction opens up new niches that eventually elicit speciation, and under conditions of relative environmental stability, specialists evolve because they are (at least temporarily) competitive under those conditions. When conditions change again, extinction ensues because not all can adapt quickly enough. Just as all individuals born in a population must eventually die, extinction is a necessary termination.
Read more »
Filed under: Hot news in climate science | 18 Comments »
 This is a general discussion thread where you can talk about whatever you like — there is nothing ‘off topic’ here — within reason. The standard commenting rules of courtesy apply, and at the very least your chat should relate to the broad theme of the blog (climate change, sustainability, energy, etc.). You can also find this thread by clicking on the Open Thread category on the left sidebar.
This is a general discussion thread where you can talk about whatever you like — there is nothing ‘off topic’ here — within reason. The standard commenting rules of courtesy apply, and at the very least your chat should relate to the broad theme of the blog (climate change, sustainability, energy, etc.). You can also find this thread by clicking on the Open Thread category on the left sidebar.





.png)


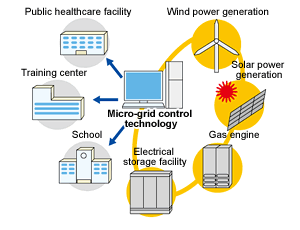
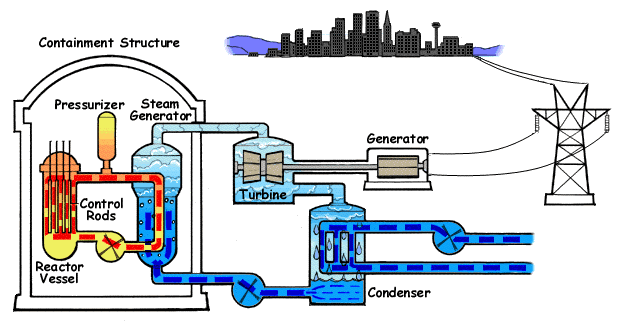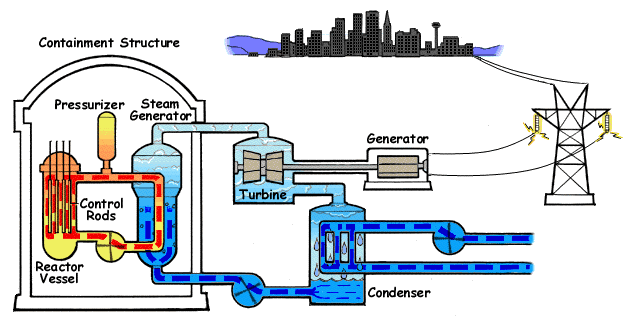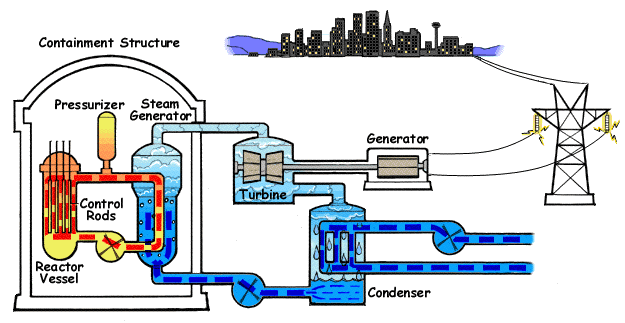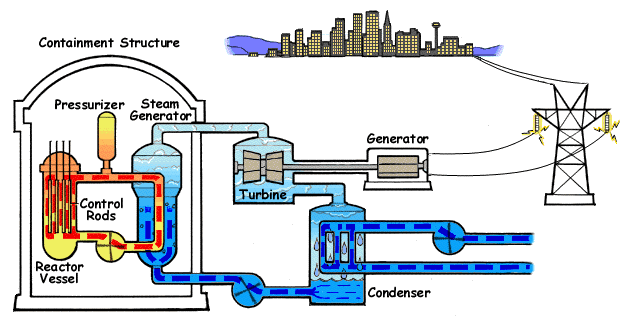

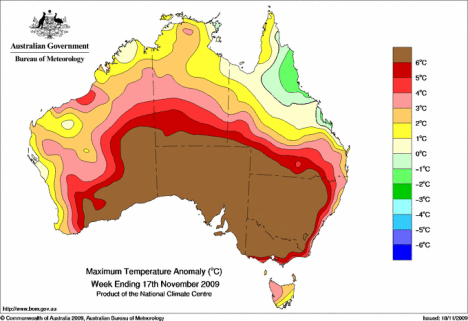





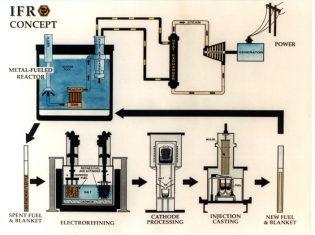
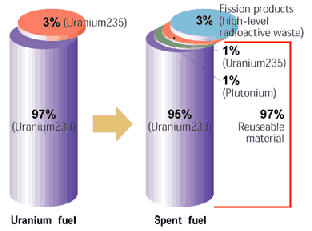
 In Australia and around the world, energy demands are on the rise. What must happen to energy generation in the face of issues such as climate change and limited fossil fuel reserves? Should power generation be localised or centralised? Researchers, governments and communities are struggling to
In Australia and around the world, energy demands are on the rise. What must happen to energy generation in the face of issues such as climate change and limited fossil fuel reserves? Should power generation be localised or centralised? Researchers, governments and communities are struggling to  agree upon the best method for future energy generation. It is an issue for everyone to consider.
agree upon the best method for future energy generation. It is an issue for everyone to consider. You will hear from Fiona Wain, Chief Executive Director of Environment Business Australia and Professor Barry Brook, Sir Hubert Wilkins Chair of Climate Change, University of Adelaide. Together with these speakers we will explore energy generation options and opportunities for Australia.
You will hear from Fiona Wain, Chief Executive Director of Environment Business Australia and Professor Barry Brook, Sir Hubert Wilkins Chair of Climate Change, University of Adelaide. Together with these speakers we will explore energy generation options and opportunities for Australia. It will commence at 5:30pm on Wednesday 11 November 2009 at Union Hall (
It will commence at 5:30pm on Wednesday 11 November 2009 at Union Hall (