I’ve talked recently on BNC about various recent energy plans. which seek to replace fossil fuels with low-carbon alternatives. On the whole, I’ve been left dissatisfied. For instance, there was the Scientific American article ‘A path to sustainable energy by 2030‘ (technology = renewables only, critiqued by me here) and the UK Royal Academy of Engineering study Generating the future: UK energy systems fit for 2050 (technology = renewables + nuclear, critiqued here). Neither pass muster, even when evaluated on general principles.
I’ve talked recently on BNC about various recent energy plans. which seek to replace fossil fuels with low-carbon alternatives. On the whole, I’ve been left dissatisfied. For instance, there was the Scientific American article ‘A path to sustainable energy by 2030‘ (technology = renewables only, critiqued by me here) and the UK Royal Academy of Engineering study Generating the future: UK energy systems fit for 2050 (technology = renewables + nuclear, critiqued here). Neither pass muster, even when evaluated on general principles.
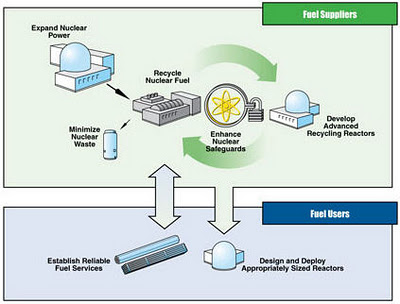
In this post, I’ll describe a third study. It provides a contrast to the other two, because it doesn’t start with the (preordained) premise that renewables and fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage WILL together do the heavy lifting. Instead, it focuses on nuclear power deployment as the primary ‘decarbonisation silver bullet’ (although other techs do play a role — perhaps an overly generous one at that). This energy map was developed by the World Nuclear Association and is called the ‘Nuclear Century Outlook‘ (NCO).
The NCO projects out 90 years, to the year 2100 — I use the term ‘project’ loosely, as really, any forecast that stretches beyond about two decades will axiomatically fall into the ‘crystal ball gazing’ category. But that’s not meant to dismiss the value in such an exercise (or others that attempt to take the long-term view). I just want to make it clear that any such long-term projection represent a ‘storyline’ (sensu IPCC SRES) rather than a ‘prediction’.
The aim of the NCO is to conceptualize nuclear power’s potential worldwide growth in the 21st Century, based on country-by-country low/high build-out assessments. Nationally aggregated data are given in tabular form here, for 2030, 2060 and 2100. The figures in this table are updated as new information comes to hand (for instance China recently upgraded their 2030 forecast from 150 to 200 GWe, and India’s 2060 goal from 350 to 500 GWe). The low/high projections are considered boundaries of a possible domain, with “low reflecting the minimum nuclear capacity expected and the high assuming a full policy commitment to nuclear power“. The forecast includes nations that currently use nuclear power, those which have expressed intention to entering the market (e.g. UAE, Egypt, Poland, Turkey) and potential future entrants (including Australia and Italy). Here is the overall projection: Read more »
Filed under: Emissions reduction, Nuclear Energy, Scenario Analysis | 460 Comments »






.png)



 To introduce the report, I’ll first reproduce the
To introduce the report, I’ll first reproduce the 
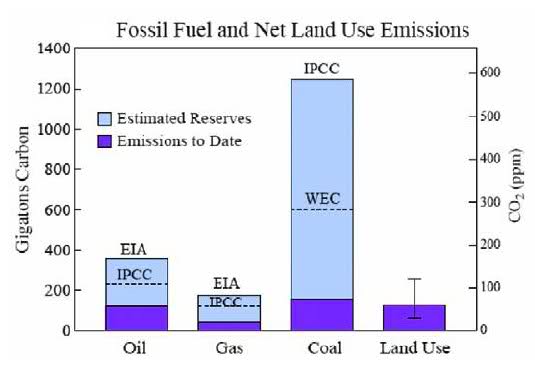 As described in
As described in 
 The
The